Osteology Case 1
You are here: > Teaching Cases and Quiz >> Osteology Case 1
Osteology Case 1
Submitted by:
Dr. Senthil R, MD, FANMB, FEBNM.
Consultant & Head – Dept. of Nuclear Medicine & PET CT,
VPS Lakeshore Hospital & Research Centre,
Kochi – 682 040, Kerala, India.
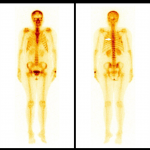
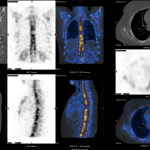
40 years old female, a known case of carcinoma of right breast underwent right mastectomy and chemotherapy. One year later she developed lung metastasis and right lung lower lobectomy was done. After 2 years the patient developed generalized body pain and was referred for Tc-99m MDP bone scan to exclude bone metastasis. What is the diagnosis, based on the whole body (white arrow) and SPECT CT images shown?
(Click on images to enlarge)
Options:
- Hemangioma
- Metastasis
- Paget’s disease
- Plasmacytoma
Scroll down for correct answer and discussion
Answer: A. Hemangioma
Explanation:
Findings: Photopenic area (cold defect) is seen in D6 vertebra, localized to body of D6 vertebra with osteopenic changes with prominent trabeculae on SPECT CT. These prominent trabecule give the “Polka dot appearance” in transaxial view and “Corduroy sign” i.e vertically-oriented, thickened trabeculae on sagittal/coronal views, consistent with hemangioma. The lesion is usually confined to vertebral body. (1)
Metastasis
Lytic metastasis appears as a cold defect on bone scintigraphy, usually with a peripheral rim of increased tracer uptake. It may appear as purely lytic lesion or mixed lytic and sclerotic lesion on CT. It may also involve posterior elements like pedicles and sometimes may have associated soft tissue component. Prominent trabeculae are not seen. (2)
Paget’s disease
This may show variable tracer uptake on bone scan, depending on the stage of the disease. Prominent trabeculae (trabecular coarsening) are also seen in Paget’s disease on CT. However it is usually associated with cortical thickening of vertebra (picture frame vertebra) and may involve entire vertebra including posterior elements. (3)
Plasmacytoma
It usually appears as a cold defect on bone scintigraphy and may have peripheral increased tracer uptake in few patients. It usually appears as purely lytic lesion. Prominent trabeculae are not seen. On radiography it may have multicystic “soap bubble” appearance. (2,4)
References:
- Liu SZ, Zhou X, Song A, Wang YP, Liu Y. The Corduroy Appearance & the Polka Dot Sign. QJM. 2019 Jul 11. pii: hcz184.
- Rodallec MH1, Feydy A, Larousserie F et al. Diagnostic imaging of solitary tumors of the spine: what to do and say. Radiographics. 2008;28(4):1019-41.
- Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Kakitsubata Y. Imaging of Paget disease of bone and its musculoskeletal complications: review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196 (6 Suppl):S64-75.
- Patnaik S, Jyotsnarani Y, Uppin SG, Susarla R. Imaging features of primary tumors of the spine: A pictorial essay. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2016;26(2):279-89.